Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
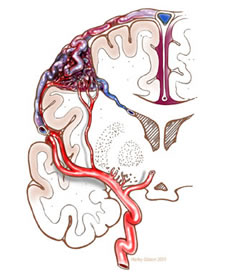 Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain which can cause bleeding in the brain, seizures, or stroke-like symptoms (weakness, numbness, tingling). The cause of AVMs is unknown.
Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of blood vessels in the brain which can cause bleeding in the brain, seizures, or stroke-like symptoms (weakness, numbness, tingling). The cause of AVMs is unknown.
Symptoms
Brain AVMs can bleed in the brain in which case patients may have a severe headache, nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, stiff neck, or loss of consciousness. They can also cause seizures. They may also cause stroke-like symptoms such as paralysis, weakness, numbness, vision problems, balance or coordination problems, or speech difficulties.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of a brain AVM is made by CT scan, MRI, and a cerebral angiogram.
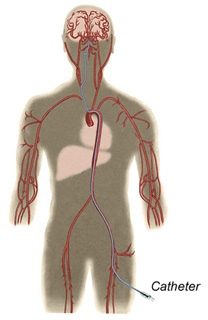
Treatment
The treatment of a brain AVM is either by surgery (opening the skull and surgically removing the AVM from the brain ), embolization (injecting substances into the AVM to block off the abnormal vessels via tiny plastic tubes inserted in the patient's groin and navigated to the brain by x-ray guidance and not requiring surgery), or radiosurgery (a one-time treatment of high-focused radiation to the brain AVM).
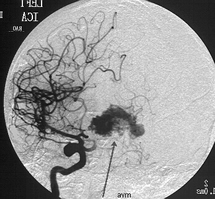 Brain AVMs are either treated after they have caused bleeding, or in some patients, an AVM is found before it has bled, and is treated to prevent it from bleeding.
Brain AVMs are either treated after they have caused bleeding, or in some patients, an AVM is found before it has bled, and is treated to prevent it from bleeding.
Prognosis
Once a patient recovers from an AVM bleeding, he or she can have a good recovery depending on the severity of the bleed and any disability caused by the bleed.