Admissions
Resources & Services
ACCORDS D&I offers interactive resources and services are for anyone, whether you have been doing D&I research for decades or are brand new our resource & services can help implement theory driven D&I practices.
Consultation
ACCORDS D&I Science and CCTSI Dissemination Service
Consultations are available for ACCORDS-affiliated faculty and staff such as School of Medicine, Children’s Hospital, and CCTSI-affiliated faculty, trainees and staff. Consultations are individual or group meetings with a D&I team member to discuss D&I methods and their application to a study. Consultations may include general discussions, education or other assistance.
We partner with the D&I Research Core led by Dr. Bethany Kwan in the Colorado Clinical and Translational Science Institute (CCTSI) at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
If you know the D&I team member you wish to contact, please still complete the consultation request form. Content area, D&I issue or questions and expertise of one of the above is the clearly best fit. If you are unclear or your request cuts across multiple D&I areas, please contact Dr. Jodi Holtrop, who will be is the primary consultation contact person and she will triage consultation requests to the most appropriate D&I team member.
We ask that you please complete the consultation request form below. This form takes less than 5 minutes to complete and is confidential. Your completed form will go to Dr. Jodi Holtrop, who will contact you within 1 week of submission to coordinate a consultation meeting.
Your consultation experience will be more efficient and productive if you think about and come prepared to share the following with the D&I team member:
- Specific question(s) and requests
- How D&I fits into your overall research proposal or work
- Extent to which your program or question is ‘ready for dissemination'
- How you anticipate evaluating D&I issues
Consultations are one to two meetings with a D&I team member to receive advice, feedback, references, provision of and connection with D&I resources, and linkage to other SOM or content expertise if relevant. Collaboration on grant proposals as a co-investigator may result from a small number of selected projects, based on the time, content area and resources of the D&I member. We do not have the time, resources or staff to be a key part of many proposals or projects requiring ongoing substantial involvement. Some K awards mentorship may be possible.
D&I Science Graduate Certificate Program
D&I Science Graduate Certificate Program
The mission of the Dissemination & Implementation Graduate Certificate Program is to equip our graduates with the D&I research skills needed to design rigorous and innovative translational research, and to successfully compete for federal funding to carry out their proposed work.
We individualize our training to address key D&I competencies and meet each trainee’s unique program goals through three key strategies:
- Maintaining small class sizes
- Using primarily synchronous online classes where faculty and students engage in rich dialogue together
- Recruiting students with diverse professional and cultural backgrounds and a variety of research experiences and goals.
Cost
FAQ
Courses
Interactive Resources
Economic, Community Engagement, Clinical, and More
Iterative PRISM Web Tool for Team Self-Assessment and Guidance
This webtool is designed for implementation teams to complete a brief survey and receive immediate feedback on their implementation progress- from the perspectives of all team members. Summary results are displayed to facilitate discussion of any adaptations needed.
Functions & Forms Webtool
This site offers information on a definition of Complex Health Interventions (CHIs), key concepts, and tools to implement and evaluate them. Information is tailored to practitioners and researchers who are new to or becoming familiar with CHIs in the healthcare and public health areas.

Co-Creation Guidebook
An introduction to co-creation for healthcare teams seeking to implement cancer control and prevention interventions. Co-creation is a scientific engagement method for developing a healthcare intervention. It brings together partners (eg., clinicians and patients) to collaborate on the design and implementation of the intervention. It harvests insights from everyone involved in the process and leads to more equitable outcomes for patients.
iPRISM and REAIM Guidebook for Planning, Implementation, and Sustainment
This guide provides direction and all the associated resources, measures, and materials in one place to successfully use Iterative PRISM and RE-AIM in an iterative manner to provide real time feedback on issues and progress in a given study, program, intervention, or project during all or a select set of phase of planning, implementation, or sustainment. Throughout this guide, we discuss possible ways in which Iterative PRISM and/or RE-AIM can be operationalized depending on the project. This method can be used to satisfy many needs throughout the phases of a project.
Implementation Science Costing Guidebook for Non-Economists
Here you will find a number of downloadable resources that we developed for our Costing Guidebook for Implementation Scientists. These resources are free to use, and they are intended for Implementation Scientists who are attempting to conduct a cost assessment on their own projects. None of these resources are finished products, and it is highly recommended that you update them according to your specific project and context, keeping in mind the principles of cost assessments described in our Guidebook.

DICEMethods.org
Ensuring research priorities, conduct, and dissemination align with stakeholder needs and perspectives is important to novice and experienced users of stakeholder engagement strategies, but this can be a challenge with so many engagement strategies to choose from. DICEMethods.org, is an Interactive Webtool and Education Hub to help you find the best strategy for your research based on five elements: purpose, budget, number of interactions, time, and staffing/expertise.

RE-AIM.org
Discover what RE-AIM is, use the interactive planning tool, get grant writing guidance, see the most recent presentations RE-AIM, and more on the RE-AIM website.

Tips for Getting Your D&I Grant Funded
Checklists, Tools, Self-ratings, and Guides for Successful Proposals in Dissemination and Implementation (D&I) Research
Resources developed by Enola Proctor, Ross Brownson, Byron Powell, Ana Baumann, Ashley Hamilton and Ryan Santens / Adapted into website form by Amy Huebschmann, Chase Cameron, Demetria McNeal, and Russell Glasgow
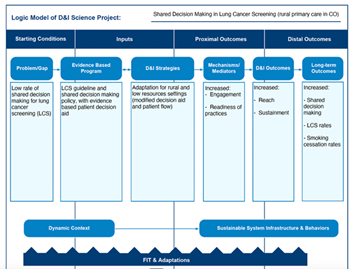
10 Key Ingredients for D&I Research Proposals
This helpful animation was developed in collaboration with colleagues from ACCORDS & CCTSI and adapted from materials presented by experts at Washington University, STL.
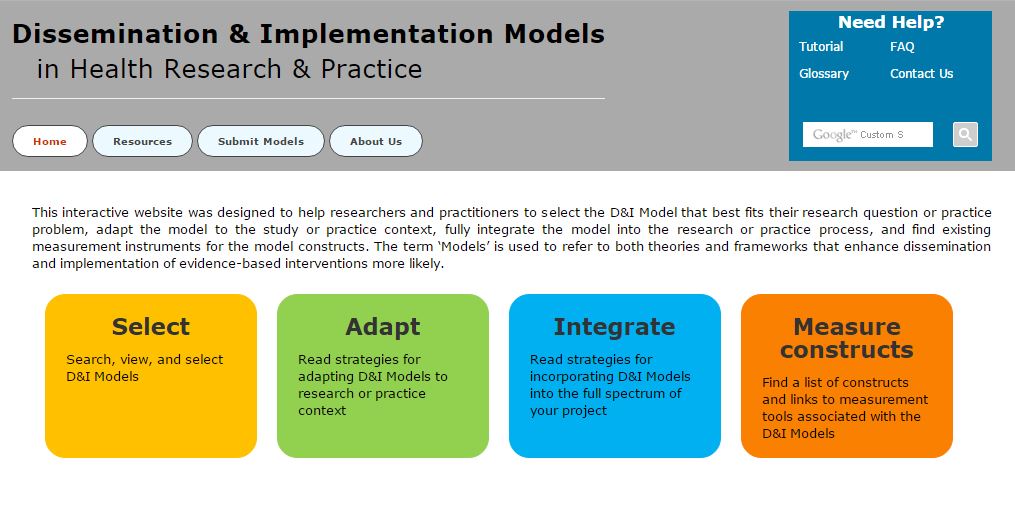
Dissemination-Implementation.org
Dissemination-Implementation.org was designed to help researchers and practitioners to select the D&I Model that best fits their research question or practice problem, adapt the model to the study or practice context, fully integrate the model into the research or practice process, and find existing measurement instruments for the model constructs. The term ‘Models’ is used to refer to both theories and frameworks that enhance the dissemination and implementation of evidence-based interventions more likely.
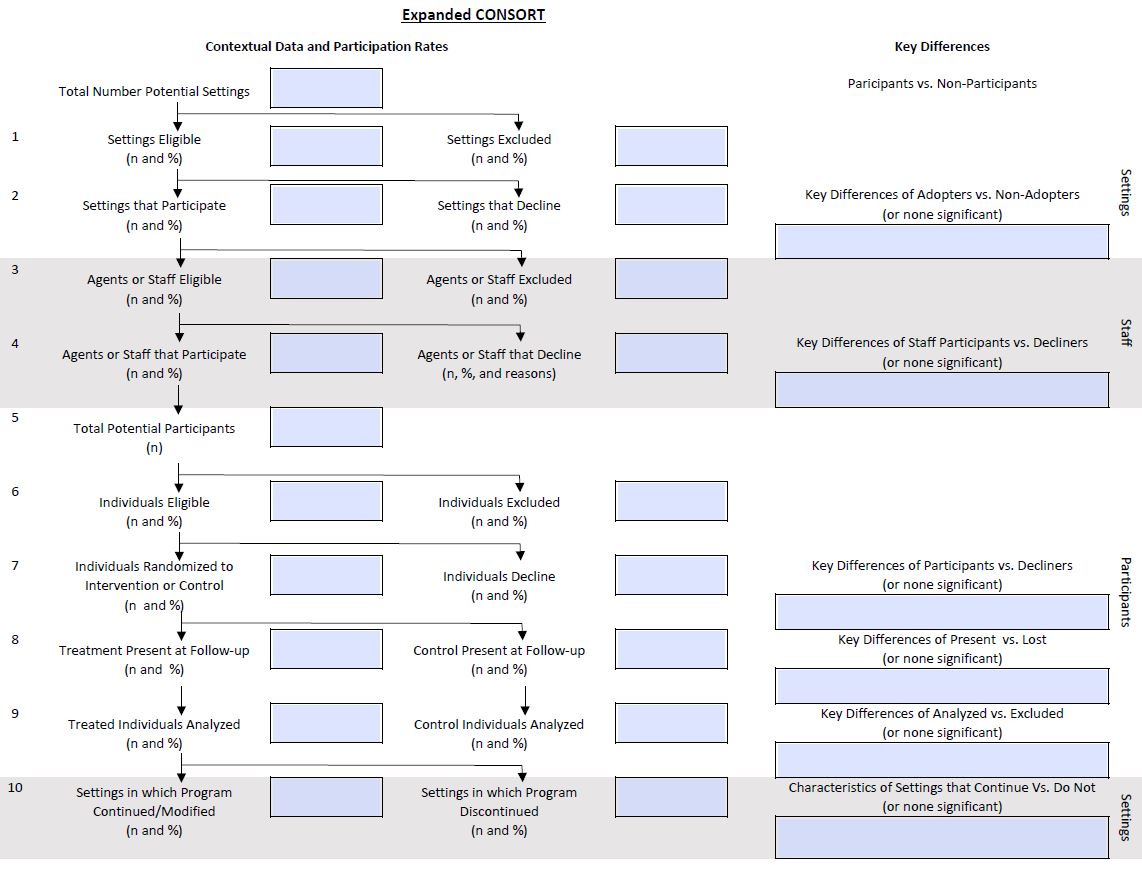
Fillable & Expanded CONSORT Figure PDF
The Expanded CONSORT expands on the Basic CONSORT flow diagram for clinical trials to summarize external validity and contextual factors more concisely and transparently. It adds data about participation and representativeness at the levels of settings and staff, and about intervention sustainability after project support ends. This figure provides a method to address the representativeness, generalizability and sustainability of outcomes research more efficiently.
FAQ
These FAQs attempt to give general answers to common questions that are asked of our D&I faculty. Some FAQs have visuals to illustrate concepts, and all have references for in-depth readings on the topic.
Beginner Resources
D&I Trainings, Courses, Conferences, Funding, and More
Annual Conference on the Science of Dissemination and Implementation in Health
AcademyHealth and the National Institutes of Health convene a meeting in December of each year to bring together the D&I Science community. The theme for the 2025 conference is: Realizing the Benefits of Dissemination & Implementation Science. The conference includes plenaries, oral and poster presentations, and interactive pre-conference workshops.
- Abstract submissions are due in mid-July.
- Proceedings, Information and resources from past conferences are available to view.
- You can learn more about this national D&I conference here.
- A select number of travel awards are available for low- and middle-income country participants whose abstracts are accepted.
US Veterans Administration Quality Enhancement Research Initiative (QUERI)
The US Veterans Administration’s QUERI Program has made many tools available on their website and offers a range of training opportunities.
- The Implementation Science resource training matrix includes a summary of the self-guided, facilitated, and mentored training tools and resources.
- QUERI Learning Hubs focus on different aspects of Implementation Science. For example, the learning hub on Implementation Facilitation offers a structured program on Implementation Facilitation which includes preparatory work, 16-hours of face-to-face or virtual training, an implementation facilitation training manual, post-training mentoring and consults, access to a learning collaborative, and CE credits.
- Other QUERI Learning Hub topics include: Adaptation; Designing for Dissemination and Implementation; Leadership and Organizational Change; and Rapid Qualitative Methods for Implementation Practice among others.
NCI’s Implementation Science Program within the Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences
The Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences of the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health is an excellent resource for funding opportunities, sample grant applications, training, and other D&I resources.
- They offer a webinar series and also archive their webinars.
- Eight modules from the Training Institute for Dissemination and Implementation Research in Cancer (TIDIRC) are available open access. The eight modules cover: Introduction to D&I Science; D&I Theories, Models and Frameworks; Measures; Study Designs; Research Approaches; Implementation Strategies; Adaptation and Fidelity; and Emerging Topics.
- Current funding opportunities and sample grant applications are available on their site.
- Implementation Science at a Glance is a helpful introductory guidebook for practitioners and policymakers.
The Center for Implementation
The Center for Implementation directed by Dr. Julia Moore and based in Toronto, Ontario, Canada is an institute that offers professional development training, implementation support and collaboration on implementation projects.
- The Inspiring Change 2.0 Mini course is a self-paced, free virtual training that provides an introduction to Implementation Science concepts.
- The Center for Implementation offers a number of other workshop topics including: sustainability and planning for spread and scale, complexity and systems thinking, adaptations, and readiness and context.
- They also provide tailored implementation support and partner on grants and projects, based on the needs of your organization.
- Their newsletter is a great way to learn about trainings and opportunities.
Suggested Readings
What We are Currently Reading
Freitas de Mello, N., Nascimento Silva, S., Gomes, D.F. et al. Models and frameworks for assessing the implementation of clinical practice guidelines: a systematic review. Implementation Sci 19, 59 (2024).
Read the Full Article Here
Villalobos, A., Reynolds, E., Halpin, S.N. et al. Prioritizing research needs and opportunities at the intersection of implementation science and engagement science. Implement Sci Commun 5, 78 (2024).
Read the Full Article Here
Strayhorn, J.C., Vanness, D.J. & Collins, L.M. Optimizing Interventions for Equitability: Some Initial Ideas. Prev Sci 25 (Suppl 3), 384–396 (2024).
Read the Full Article Here
Squires, J.E., Graham, I.D., Santos, W.J. et al. The Implementation in Context (ICON) Framework: A meta-framework of context domains, attributes and features in healthcare. Health Res Policy Sys 21, 81 (2023).
Read the Full Article Here
Our Presentations
Select PowerPoint Presentations
Methods and Measures to Understand Context
Panel Presentation at the 17th Annual Conference on the Science of Dissemination and Implementation in Health
Presenters: Mustafa Ozkaynak, Bethany Kwan, Heather Gilmartin and Edmond Ramly
Key content: The panel discussed challenges of measuring context, identifying effective implementation strategies, adaptations, and ensuring fit to context, and highlighted four pragmatic approaches. The tension between pragmatism and rigor was also discussed.
View "Methods to Measure and Understand Context" Presentations
Adaptation, Fidelity, and Tailoring Workgroup
Presenter: Mónica Pérez Jolles, Novemeber 2024
Key content: This presentation is on "Complex interventions: Introduction of a webtool to identify and track core functions and forms".
Watch "Adaptation, Fidelity, and Tailoring Workgroup" on YouTube
D&I Meeting Recordings
This section is under development. Please check back again later.
This section is under construction, please check back later.