Welcome to Neurology Clinical Research!
Message to UCDenver Faculty and Staff:
Neurology is one of the largest clinical research enterprises in the University of Colorado School of Medicine, with over 333 active research studies/clinical trials
in different phases of completion (study start-up, enrolling new participants, and follow-up of current participants). Our program includes over 92 staff
who manage our research studies/clinical trials day-to-day. Additionally, our worldwide collaborators include experts from academic institutions and leaders in the clinical research field. In 2023, we had an average of 1,460 recruitment communications (phone, email, in-person contact, etc.) per month and 3,511 clinical research participant visits in
total - a 24% increase from 2022!
Neurology Clinical Research Study Statuses CY 2024
*69% Non-Industry Funded, 31% Industry Funded

| Neurology Clinical Research Study Statuses CY 2024 | |
| Active, Closed to Accrual | 79 |
| Active, Open to Accrual | 136 |
| In Start-Up | 60 |
| Secondary Use | 97 |
| CY Total | 372 |
Neurology Clinical Research CY 2020-2024 Growth Comparison

| All Studies Statuses | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Active, Closed to Accrual | 47 | 61 | 54 | 63 | 79 |
| Active, Open to Accrual | 118 | 147 | 184 | 126 | 136 |
| In Start-Up | 53 | 49 | 55 | 48 | 60 |
| Secondary Use | N/A | N/A | N/A | 96 | 97 |
| CY Total | 218 | 257 | 293 | 333 | 372 |
Subspecialty CY 2024 Statistics
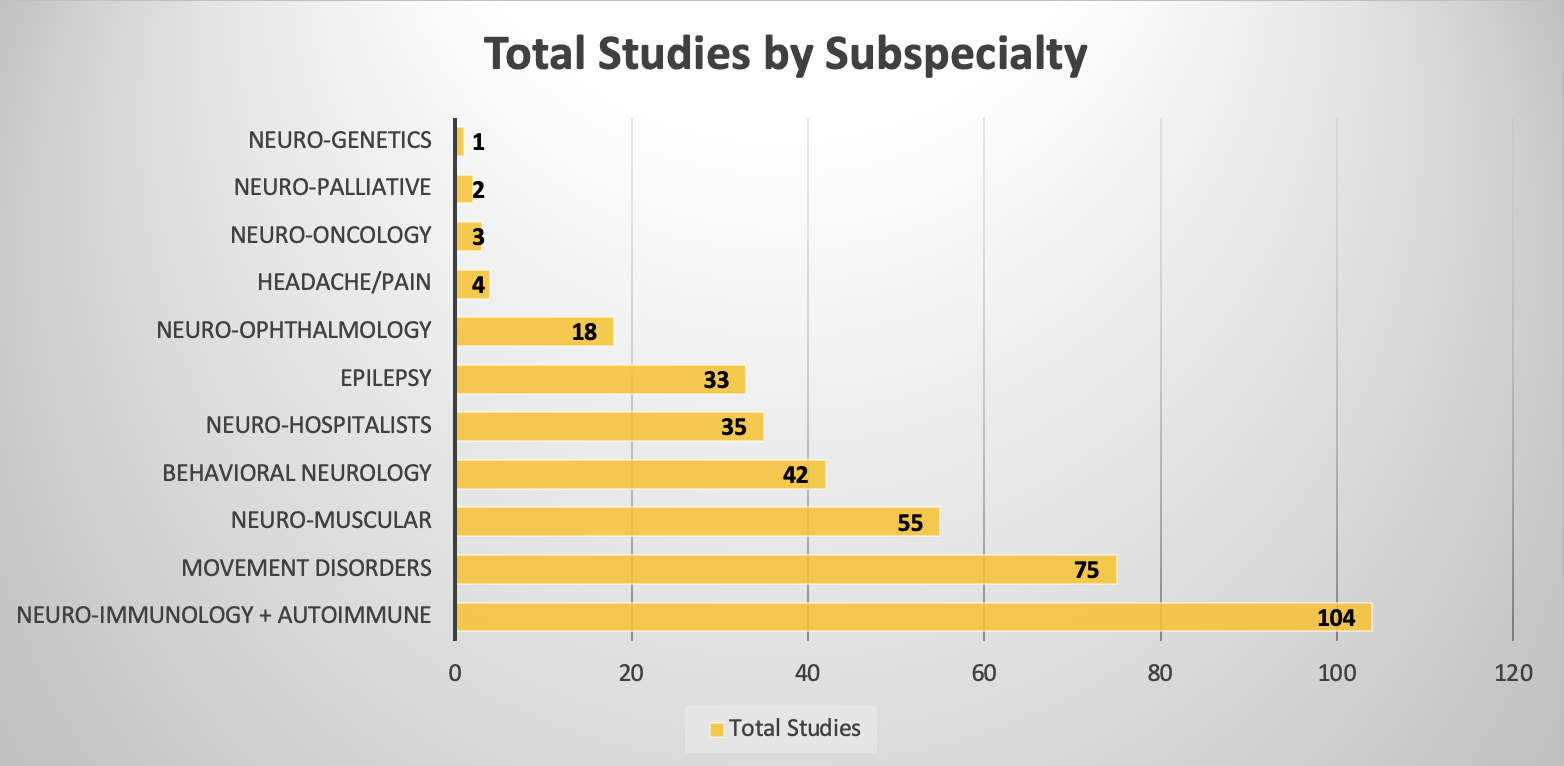
| Subspecialty | Total Studies: 372 |
| Behavioral Neurology | 42 |
| Epilepsy | 33 |
| Headache/Pain | 4 |
| Movement Disorders | 75 |
| Neuro-Genetics | 1 |
| Neuro-Hospitalists | 35 |
| Neuro-Immunology + Autoimmune | 104 |
| Neuro-Muscular | 55 |
| Neuro-Oncology | 3 |
| Neuro-Ophthalmology | 18 |
| Neuro-Palliative | 2 |
We offer a variety of Clinical Research:
- Drug Studies
- Non-drug Treatments and Interventions
- Device Studies
- Observational (blood draw studies, questionnaire studies)
- Biobanking
- Patient-reported Outcomes
- Imaging (MEG, MRI, fMRI, PET scan)
- Quality Improvements
- Translational Lab and Tissue Bank
Explore our Neurology Research Laboratories:
- Alzheimer's Disease and Cognition
- CU Neuro-Magnetic Laboratories
- Neuroimmunology: Autoimmune Inflammatory Disorders of the Central Nervous System
- Neurovirology: Role of Varicella Zoster Virus in the Central Nervous System
- Neurovirology: Epigenetic Regulation of Varicella Zoster Virus
- Neurovirology: In Vivo Models of Varicella-Zoster Virus Neurotropism
- Neurovirology: Virus Infections of the Central Nervous System
 Image: Anschutz Health Sciences Building (AHSB), the location of our outpatient Clinical and Translational Research Center (CTRC).
Image: Anschutz Health Sciences Building (AHSB), the location of our outpatient Clinical and Translational Research Center (CTRC).
New to Clinical Research?
Learn more about clinical research by visiting the following resources:
- What are Research Studies? by the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Research Studies Team
- The Center for Information and Study on Clinical Research Participation (CISCRP) is first-of-its-kind nonprofit organization dedicated to educating and informing the public, patients,
medical/research communities, the media, and policy makers about clinical research and the role each party plays in the process.
- The CISCRP Community Resources webpage contains a number of contact information-containing resources available to anyone seeking information about clinical research, both general and disease-specific.
- Clinicaltrials.gov Glossary of Common Site Terms
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) - Clinical Trails and You
- PubMed is a free (as in money) resource supporting the search and retrieval of biomedical and life sciences literature with the aim of improving health–both globally and personally.
Common Terms:
- Arm: a group or subgroup of participants in a clinical trial that receives a specific intervention/treatment, or no intervention, according to the trial's protocol.
- Clinical study: a research study involving human volunteers (also called participants) that is intended to add to medical knowledge. There are two types of clinical studies: interventional studies (also called clinical trials) and observational studies.
- Clinical trial: another name for an interventional study.
- ClinicalTrials.gov identifier (NCT number): the unique identification code given to each clinical study upon registration at ClinicalTrials.gov. The format is "NCT" followed by an 8-digit number (for example, NCT00000419).
- Eligibility criteria: the key requirements that people who want to participate in a clinical study must meet or the characteristics they must have. Eligibility criteria consist of both inclusion criteria (which are required for a person to participate in the study) and exclusion criteria (which prevent a person from participating). Types of eligibility criteria include whether a study accepts healthy volunteers, has age or age group requirements, or is limited by sex.
- Informed consent: a process used by researchers to communicate to potential and enrolled participants the risks and potential benefits of participating in a clinical study.
- Intervention/treatment: a process or action that is the focus of a clinical study. Interventions include drugs, medical devices, procedures, vaccines, and other products that are either investigational or already available. Interventions can also include noninvasive approaches, such as education or modifying diet and exercise.
- Observational study: a type of clinical study in which participants are identified as belonging to study groups and are assessed for biomedical or health outcomes. Participants may receive diagnostic, therapeutic, or other types of interventions, but the investigator does not assign participants to a specific interventions/treatment.
- Placebo: an inactive substance or treatment that looks the same as, and is given in the same way as, an active drug or intervention/treatment being studied.
- Principal Investigator (PI): the person who is responsible for the scientific and technical direction of the entire clinical study.
- Protocol: the written description of a clinical study. It includes the study's objectives, design, and methods. It may also include relevant scientific background and statistical information.
- Research Services Professional (RSP): the title of clinical research coordinators at the University of Colorado. The RSP coordinates research visits and helps the PI carefully manage the participant’s care.
- Sponsor: the organization or person who initiates the study and who has authority and control over the study.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting the public health by making sure that human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products, medical devices, the Nation's food supply, cosmetics, dietary supplements, and products that give off radiation are safe, effective, and secure.
*all above definitions were copied from the Clinicaltrials.gov Glossary of Common Site Terms
Research is critical in helping to advance our knowledge of neurological diseases in order to best care for our patients. We also welcome Healthy Volunteers to participate in our studies! Join us and become a part of the Neurology Clinical Research family as we aim to become a Center of Research Excellence!
For questions about our clinical research, please contact the Neurology Research Recruitment Team at 303-724-4644 or [email protected] .
Local Neurology Events
No events currently scheduled.
Clinical Research by Subspecialty
Neuroimmunology
Autoimmune Encephalitis, Bio and Tissue Banks, Exercise Studies, First-degree Relatives of People with Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Healthy Volunteer Studies, Newly Diagnosed MS, Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (PPMS), and Relapsing and Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (RSPMS).
Click to explore!
Movement Disorders
Ataxia, Dystonia, Huntington’s Disease (HD), Multiple System Atrophy-Parkinsonian subtype (MSA-P), and Parkinson’s Disease (PD).
Click to explore!
Neurobehavior
Alzheimer's Disease (AD), Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD), Lewy Body Dementia (LBD), and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI).
Click to explore!
Neuromuscular
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD), Charcot Marie Tooth Disease (CMT), Diabetic Neuropathy (DN), Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD), Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy (LGMD), Myasthenia Gravis (MG), Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1), and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA).
Click to explore!
Epilepsy
Focal Epilepsy, Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy (IGE), Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure (PGTCS), and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (TLE).
Click to explore!
Get Connected
If you think you may be eligible for one of these studies or if you would like more information, please fill out our Neurology Research Interest Web Form or contact us at N[email protected] or 303-724-4644.