Research
Our laboratory is interested in the development and application of advanced genome technologies, particularly as they apply to our understanding of human disease and evolution. Areas of special interest include the identification of genetic factors involved in neurogenetic diseases such as microcephaly, macrocephaly, autism and schizophrenia, and the use of novel evolutionary genomics approaches to identify genes and genome structural variations unique to the human and great ape lineages. Technologies that are used include nextgen DNA sequencing, custom array-based comparative genomic hybridization (arrayCGH), and novel bioinformatics tools for the rapid identification of genes and copy number variations (CNVs) underlying complex human diseases and lineage-specific traits. These approaches are also being tailored to allow the study and copy number discrimination of highly duplicated genome sequences, such as those that reside in 1q21.1 and other complex and dynamic regions of the human genome.
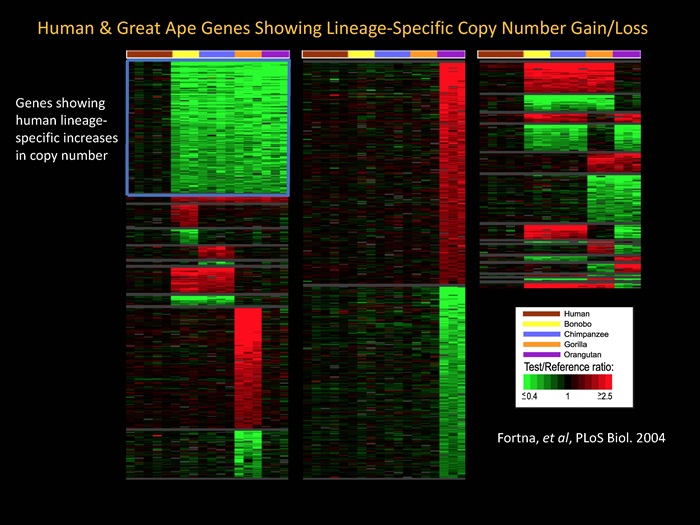
Evolutionary genomics and human brain evolution: To gain insights into the evolutionary genomics of human and great ape lineages, we are using arrayCGH to identify lineage-specific gene duplications or losses that have occurred between these lineages. Of particular interest are those human lineage-specific genes that underlie human specific traits, such as the cognitive abilities unique to the human brain, and how such genes, when defective, lead to cognitive disability. Of special interest are DUF1220 protein domains (now called Olduvai domains) which we have shown are dramatically increased in copy number in the human lineage and may be important to both human brain evolution and recurrent cognitive disease.