Shared Content Block:
Styles -- prevent images from going to 100 percent width on mobile
Research Highlights
A brief look at the latest discoveries from RBI faculty and trainees.
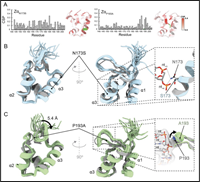
Differential structural features of two mutant ADAR1p150 Zα domains cause Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome
March 6, 2023
Conner J Langeberg, Parker J Nichols, Morkos A Henen, Quentin Vicens, Beat Vögeli
The Zα domain of ADARp150 is critical for proper Z-RNA substrate binding and is a key factor in the type-I interferon response pathway. Two point-mutations in this domain (N173S and P193A), which cause neurodegenerative disorders, are linked to decreased A-to-I editing in disease models. To understand this phenomenon at the molecular level, we biophysically and structurally characterized these two mutated domains, revealing that they bind Z-RNA with a decreased affinity.
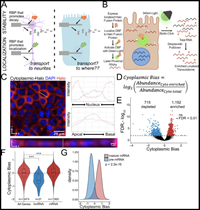
RNA localization mechanisms transcend cell morphology
March 3, 2023
Raeann Goering, Ankita Arora, Megan C Pockalny, J Matthew Taliaferro
RNA molecules are localized to specific subcellular regions through interactions between RNA regulatory elements and RNA binding proteins (RBPs). Generally, our knowledge of the mechanistic details behind the localization of a given RNA is restricted to a particular cell type. Here, we show that RNA/RBP interactions that regulate RNA localization in one cell type predictably regulate localization in other cell types with vastly different morphologies. To determine transcriptome-wide RNA spatial distributions across the apicobasal axis of human intestinal epithelial cells, we used our recently developed RNA proximity labeling technique, Halo-seq. We found that mRNAs encoding ribosomal proteins (RP mRNAs)...
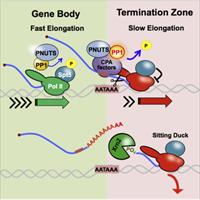
October 6, 2022
Nova Fong, Ryan M Sheridan, Srinivas Ramachandran, David L Bentley
The pause-release model of transcription proposes that 40-100 bases from the start site RNA Pol II pauses, followed by release into productive elongation. Pause release is facilitated by the PTEFb phosphorylation of the RNA Pol II elongation factor, Spt5. We mapped paused polymerases by eNET-seq and found frequent pausing in zones that extend ∼0.3-3 kb into genes even when PTEFb is inhibited. The fraction of paused polymerases or pausing propensity declines gradually over several kb and not abruptly as predicted for a discrete pause-release event.
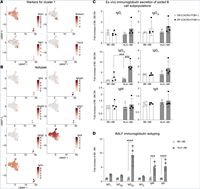
September 22, 2022
Natalia F Smirnova, Kent Riemondy, Marta Bueno, Susan Collins, Pavan Suresh, Xingan Wang, Kapil N Patel, Carlyne Cool, Melanie Königshoff, Nirmal S Sharma, Oliver Eickelberg
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is the main reason for poor outcomes after lung transplantation (LTx). We and others have recently identified B cells as major contributors to BOS after LTx. The extent of B cell heterogeneity and the relative contributions of B cell subpopulations to BOS, however, remain unclear. Here, we provide a comprehensive analysis of cell population changes and their gene expression patterns during chronic rejection after...
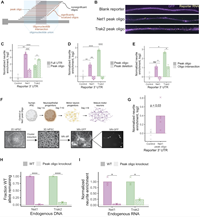
High-throughput identification of RNA localization elements in neuronal cells
September 15, 2022
Ankita Arora, Roberto Castro-Gutierrez, Charlie Moffatt, Davide Eletto, Raquel Becker, Maya Brown, Andreas E Moor, Holger A Russ, J Matthew Taliaferro
Hundreds of RNAs are enriched in the projections of neuronal cells. For the vast majority of them, though, the sequence elements that regulate their localization are unknown. To identify RNA elements capable of directing transcripts to neurites, we deployed a massively parallel reporter assay that tested the localization regulatory ability of thousands of sequence fragments drawn from endogenous mouse 3' UTRs. We identified peaks of regulatory activity within several 3' UTRs and found that sequences derived from these peaks were both necessary…
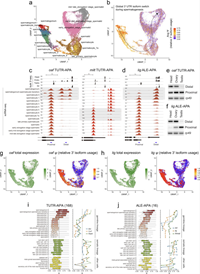
Diverse cell-specific patterns of alternative polyadenylation in Drosophila
September 13, 2022
Seungjae Lee, Yen-Chung Chen, FCA Consortium, Austin E Gillen, J Matthew Taliaferro, Bart Deplancke, Hongjie Li, Eric C Lai
Most genes in higher eukaryotes express isoforms with distinct 3' untranslated regions (3' UTRs), generated by alternative polyadenylation (APA). Since 3' UTRs are predominant locations of post-transcriptional regulation, APA can render such programs conditional, and can also alter protein sequences via alternative last exon (ALE) isoforms. We previously used 3'-sequencing from diverse Drosophila samples to define multiple tissue-specific APA landscapes. Here, we exploit comprehensive single nucleus RNA-sequencing data (Fly Cell Atlas) to elucidate cell-type expression of 3' UTRs across >250 adult Drosophila cell types. We reveal the cellular bases of multiple tissue-specific APA/ALE programs, such as 3' UTR lengthening in differentiated neurons and 3' UTR shortening in spermatocytes and spermatids.
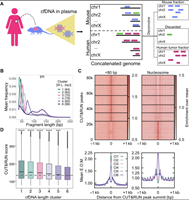
August 26, 2022
Satyanarayan Rao, Amy L Han, Alexis Zukowski, Etana Kopin, Carol A Sartorius, Peter Kabos, Srinivas Ramachandran
Genome-wide binding profiles of estrogen receptor (ER) and FOXA1 reflect cancer state in ER+ breast cancer. However, routine profiling of tumor transcription factor (TF) binding is impractical in the clinic. Here, we show that plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) contains high-resolution ER and FOXA1 tumor binding profiles for breast cancer. Enrichment of TF footprints in plasma reflects the binding strength of the TF in originating tissue. We defined pure in vivo tumor TF signatures in plasma using ER+ breast cancer xenografts, which can distinguish...
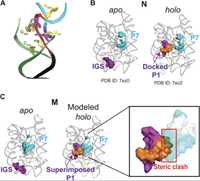
Cryo-EM reveals an entangled kinetic trap in the folding of a catalytic RNA
August 26, 2022
Steve L Bonilla, Quentin Vicens, Jeffrey S Kieft
Functional RNAs fold through complex pathways that can contain misfolded "kinetic traps." A complete model of RNA folding requires understanding the formation of these misfolded states, but they are difficult to characterize because of their transient and potentially conformationally dynamic nature. We used cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to visualize a long-lived misfolded state in the folding pathway of the Tetrahymena thermophila group I intron, a paradigmatic RNA structure-function model system. The structure revealed how this state forms ...
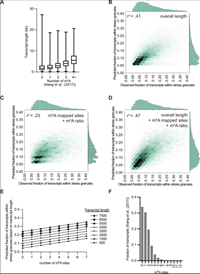
Limited effects of m6A modification on mRNA partitioning into stress granules
June 29, 2022
Anthony Khong, Tyler Matheny, Thao Ngoc Huynh, Vincent Babl, Roy Parker
The presence of the m6A modification in mammalian mRNAs is proposed to promote mRNA recruitment to stress granules through the interaction with YTHDF proteins. We test this possibility by examining the accumulation of mRNAs in stress granules in both WT and ∆METTL3 mES cells, which are deficient in m6A modification. A critical observation is that all m6A modified mRNAs partition similarly into stress granules in both wild-type and m6A-deficient cells by single-molecule FISH. Moreover, multiple linear regression analysis indicates m6A modification explains only 6% of the variance in stress granule localization when controlled for length. Finally, the artificial tethering of 25...
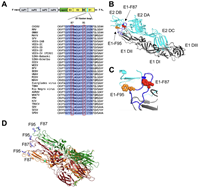
April 13, 2022
Cormac J Lucas, Bennett J Davenport, Kathryn S Carpentier, Alex N Tinega, Thomas E Morrison
Alphaviruses infect cells by a low pH-dependent fusion reaction between viral and host cell membranes that is mediated by the viral E1 glycoprotein. Most reported alphavirus E1 sequences include two phenylalanines (F87 and F95) in the fusion loop, yet the role of these residues in viral infectivity remains to be defined. Following introduction of wild type (WT), E1-F87A, and E1-F95A chikungunya virus (CHIKV) RNA genomes into cells...
Small RNA pathways in the nematode Ascaris in the absence of piRNA
February 11, 2022
Maxim V. Zagoskin, Jianbin Wang, Ashley T. Neff, Giovana M. B. Veronezi, Richard E. Davis
Precise gene models using long-read sequencing reveal a unique poly(A) signal in Giardia lamblia
February 2, 2022
Danielle Y Bilodeau, Ryan M Sheridan, Balu Balan, Aaron R Jex, Olivia S Rissland
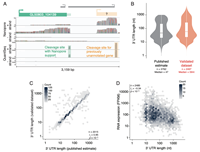
During pre-mRNA processing, the poly(A) signal is recognized by a protein complex that ensures precise cleavage and polyadenylation of the nascent transcript. The location of this cleavage event establishes the length and sequence of the 3' UTR of an mRNA, thus...
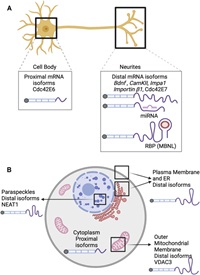
The role of alternative polyadenylation in the regulation of subcellular RNA localization
January 14, 2022
Ankita Arora, Raeann Goering, Hei Yong G Lo, Joelle Lo, Charlie Moffatt, J Matthew Taliaferro
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is a widespread and conserved regulatory mechanism that generates diverse 3' ends on mRNA. APA patterns are often tissue specific and play an important role in cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and response to stress. Many APA sites are found in 3' UTRs, generating mRNA isoforms with different 3' UTR contents.
These alternate 3' UTR isoforms can change how the transcript is regulated, affecting its stability and translation. Since the subcellular localization of a transcript is often regulated by 3' UTR…
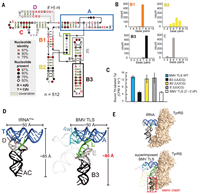
A viral RNA hijacks host machinery using dynamic conformational changes of a tRNA-like structure
November 19, 2021
Steve L Bonilla, Madeline E Sherlock, Andrea MacFadden, Jeffrey S Kieft
Viruses require multifunctional structured RNAs to hijack their host’s biochemistry, but their mechanisms can be obscured by the difficulty of solving conformationally dynamic RNA structures. Using cryo–electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we visualized the structure of the mysterious viral transfer RNA (tRNA)–like structure (TLS) from the brome mosaic virus, which affects replication, translation, and genome encapsidation. Structures in isolation and those bound to tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (TyrRS) show...

October 7, 2021
Kathryn S Carpentier, Ryan M Sheridan, Cormac J Lucas, Bennett J Davenport, Frances S Li, Erin D Lucas, Mary K McCarthy, Glennys V Reynoso, Nicholas A May, Beth A J Tamburini, Jay R Hesselberth, Heather D Hickman, Thomas E Morrison
Viremia in the vertebrate host is a major determinant of arboviral reservoir competency, transmission efficiency, and disease severity. However, immune mechanisms that control arboviral viremia are poorly defined. Here, we identify critical roles for the scavenger receptor MARCO in controlling viremia during arthritogenic alphavirus infections in mice. Following subcutaneous inoculation, arthritogenic alphavirus particles drain via the lymph and are...
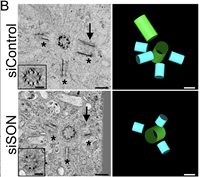
October 1, 2021
Alexander J Stemm-Wolf, Eileen T O'Toole, Ryan M Sheridan, Jacob T Morgan, Chad G Pearson
Control of centrosome assembly is critical for cell division, intracellular trafficking, and cilia. Regulation of centrosome number occurs through the precise duplication of centrioles that reside in centrosomes. Here we explored transcriptional control of centriole assembly and find that the RNA splicing factor SON is specifically required for completing procentriole assembly.
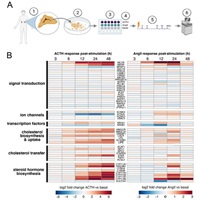
September 9, 2021
Kimberly Wellman, Rui Fu, Amber Baldwin, Juilee Rege, Elisabeth Murphy, William E Rainey, Neelanjan Mukherjee
Adrenal steroid hormone production is a dynamic process stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and angiotensin II (AngII). These ligands initialize a rapid and robust gene expression response required for steroidogenesis. Here, we compare the predominant human immortalized cell line model, H295R cell, with primary cultures of adult adrenocortical cells derived...
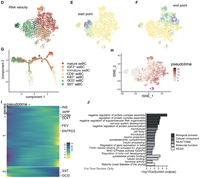
ENTPD3 marks mature stem cell derived beta cells formed by self-aggregation in vitro
August 11, 2021
Fiona M Docherty, Kent A Riemondy, Roberto Castro-Gutierrez, JaeAnn M Dwulet, Ali H Shilleh, Maria S Hansen, Shane P M Williams, Lucas H Armitage, Katherine E Santostefano, Mark A Wallet, Clayton E Mathews, Taylor M Triolo, Richard K P Benninger, Holger A Russ
Stem cell derived beta-like cells (sBC) carry the promise of providing an abundant source of insulin-producing cells for use in cell replacement therapy for patients with diabetes, potentially allowing widespread implementation of a practical cure. To achieve their clinical promise, sBC need to function comparably to mature adult beta cells, but as yet they display varying degrees of maturity...
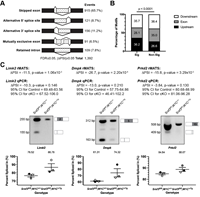
Srsf3 mediates alternative RNA splicing downstream of PDGFRα signaling in the facial mesenchyme
July 15, 2021
Brenna J C Dennison, Eric D Larson, Rui Fu, Julia Mo, Katherine A Fantauzzo
Signaling through the platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα) is crucial for mammalian craniofacial development, although the mechanisms by which the activity of downstream intracellular effectors is regulated to mediate gene expression changes have not been defined. We find that the RNA-binding protein Srsf3 is phosphorylated at Akt consensus sites downstream of PI3K-mediated PDGFRα signaling in mouse palatal mesenchyme cells, leading to its nuclear translocation.
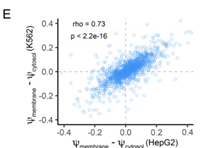
June 26, 2021
Raeann Goering, Krysta L Engel, Austin E Gillen, Nova Fong, David L Bentley, J Matthew Taliaferro
The sequence content of the 3' UTRs of many mRNA transcripts is regulated through alternative polyadenylation (APA). The study of this process using RNAseq data, though, has been historically challenging.
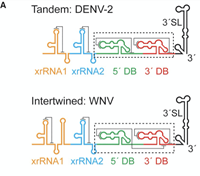
June 16, 2021
Benjamin M Akiyama, Monica E Graham, Zoe O Donoghue, J David Beckham, Jeffrey S Kieft
Mosquito-borne flaviviruses (MBFVs) including dengue, West Nile, yellow fever, and Zika viruses have an RNA genome encoding one open reading frame flanked by 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTRs). The 3' UTRs of MBFVs contain regions of high sequence conservation in structured RNA elements known as dumbbells (DBs).
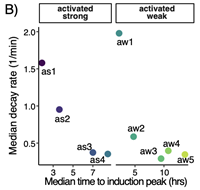
RNA-binding proteins regulate aldosterone homeostasis in human steroidogenic cells
June 1, 2021
Rui Fu, Kimberly Wellman, Amber Baldwin, Juilee Rege, Kathryn Walters, Antje Hirsekorn, Kent Riemondy, William E Rainey and Neelanjan Mukherjee
Angiotensin II (AngII) stimulates adrenocortical cells to produce aldosterone, a master regulator of blood pressure. Despite extensive characterization of the transcriptional and enzymatic control of adrenocortical steroidogenesis, there are still major gaps in the precise regulation of AII-induced gene expression kinetics.
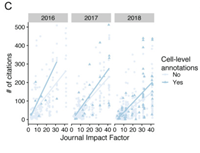
Cell-level metadata are indispensable for documenting single-cell sequencing datasets
May 24, 2021
Sidhant Puntambekar, Jay R Hesselberth, Kent A Riemondy, Rui Fu
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has empowered discoveries of cell heterogeneity and state transitions at unprecedented resolution and throughput. New technological developments have broadened the scope of measurable molecules, extending beyond RNA to measure cell surface proteins.
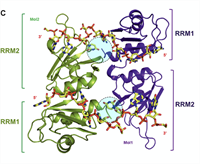
Establishing RNA-RNA Interactions Remodels lncRNA Structure and Promotes PRC2 Activity
April 14, 2021
Maggie M. Balas, Erik W. Hartwick, Chloe Barrington, Justin T. Roberts, Stephen K. Wu, Ryan Bettcher, April M. Griffin, Jeffrey S. Kieft, Aaron M. Johnson
Human Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) catalysis of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation at certain loci depends on long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). Yet, in apparent contradiction, RNA is a potent catalytic inhibitor of PRC2. Here, we show that intermolecular RNA-RNA interactions between the lncRNA HOTAIR and its targets can relieve RNA inhibition of PRC2.
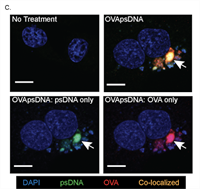
Molecular Tracking Devices Quantify Antigen Distribution and Archiving in the Murine Lymph Node
April 12, 2021
Shannon M Walsh, Ryan M Sheridan, Erin D Lucas, Thu A Doan, Brian C Ware, Johnathon Schafer, Rui Fu, Matthew A Burchill, Jay R Hesselberth, Beth Ann Jiron Tamburini
The detection of foreign antigens in vivo has relied on fluorescent conjugation or indirect read-outs such as antigen presentation. In our studies, we found that these widely used techniques had several technical limitations that have precluded a complete picture of antigen trafficking or retention across lymph node cell types.
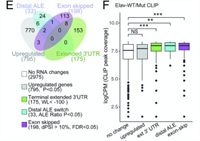
ELAV/Hu RNA Binding Proteins Determine Multiple Programs of Neural Alternative Splicing
April 7, 2021
Seungjae Lee, Lu Wei, Binglong Zhang, Raeann Goering, Sonali Majumdar, Jiayu Wen, J Matthew Taliaferro, Eric C Lai
ELAV/Hu factors are conserved RNA binding proteins (RBPs) that play diverse roles in mRNA processing and regulation. The founding member, Drosophila Elav, was recognized as a vital neural factor 35 years ago. Nevertheless, little was known about its impact on the transcriptome, and potential functional overlap with its paralogs.
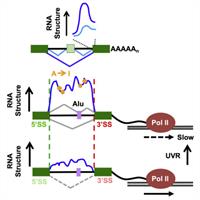
February 24, 2021
Tassa Saldi, Kent Riemondy, Benjamin Erickson, and David L. Bentley
Most RNA processing occurs co-transcriptionally. We interrogated nascent pol II transcripts by chemical and enzymatic probing and determined how the “nascent RNA structureome” relates to splicing, A-I editing and transcription speed. RNA folding within introns and steep structural transitions at splice sites are associated with efficient co-transcriptional splicing.
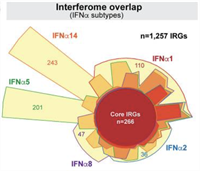
October 16, 2020
Kejun Guo, Guannan Shen, Jon Kibbie, Tania Gonzalez, Stephanie M Dillon, Harry A Smith, Emily H Cooper, Kerry Lavender, Kim J Hasenkrug, Kathrin Sutter, Ulf Dittmer, Miranda Kroehl, Katerina Kechris, Cara C Wilson and Mario L Santiago
The Type I Interferons (IFN-Is) are innate antiviral cytokines that include 12 different IFNα subtypes and IFNβ that signal through the IFN-I receptor (IFNAR), inducing hundreds of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) that comprise the 'interferome'.
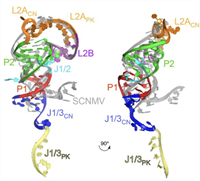
August 26, 2020
Anna-Lena Steckelberg, Quentin Vicens, David A. Costantino, Jay C. Nix and Jeffrey S. Kieft
Exoribonuclease-resistant RNAs (xrRNAs) are discrete elements that block the progression of 5′ to 3′ exoribonucleases using specifically folded RNA structures. A recently discovered class of xrRNA is widespread in several genera of plant-infecting viruses, within both...

JMJD5 couples with CDK9 to release the paused RNA polymerase II
August 18, 2020
Haolin Liu, Srinivas Ramachandran, Nova Fong, Tzu Phang, Schuyler Lee, Pirooz Parsa, Xinjian Liu, Laura Harmacek, Thomas Danhorn, Tengyao Song, Sangphil Oh, Qianqian Zhang, Zhongzhou Chen, Qian Zhang, Ting-Hui Tu, Carrie Happoldt, Brian O'Conner, Ralf Janknecht, Chuan-Yuan Li, Philippa Marrack, John Kappler, Sonia Leach and Gongyi Zhang
More than 30% of genes in higher eukaryotes are regulated by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) promoter proximal pausing. Pausing is released by the positive transcription elongation factor complex (P-TEFb).
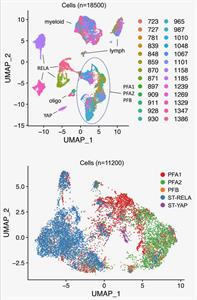
August 11, 2020
Austin E Gillen, Kent A Riemondy, Vladimir Amani, Andrea M Griesinger, Ahmed Gilani, Sujatha Venkataraman, Krishna Madhavan, Eric Prince, Bridget Sanford, Todd C Hankinson, Michael H Handler, Rajeev Vibhakar, Ken L Jones, Siddhartha Mitra, Jay R Hesselberth, Nicholas K Foreman and Andrew M Donson
Ependymoma (EPN) is a brain tumor commonly presenting in childhood that remains fatal in most children. Intra-tumoral cellular heterogeneity in bulk-tumor samples significantly confounds our understanding of EPN biology, impeding development of effective therapy. We, therefore, use single-cell RNA sequencing, histology, and deconvolution to catalog cellular heterogeneity of the major childhood EPN subgroups.
Simultaneous Measurement of Biochemical Phenotypes and Gene Expression in Single Cells
June 4, 2020
Amanda L Richer, Kent A Riemondy, Lakotah Hardie and Jay R Hesselberth
Methods to measure heterogeneity among cells are rapidly transforming our understanding of biology but are currently limited to molecular abundance measurements. We developed an approach to simultaneously measure biochemical activities and mRNA abundance in single cells...
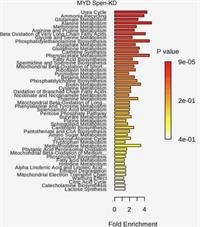
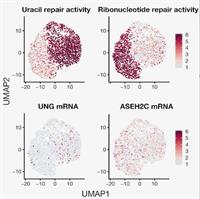
Gene–Diet Interactions: Dietary Rescue of Metabolic Defects in spen-Depleted Drosophila melanogaster
April 1, 2020
Claire M. Gillette, Kelsey E. Hazegh, Travis Nemkov, Davide Stefanoni, Angelo D’Alessandro, J. Matthew Taliaferro and Tania Reis
Obesity and its comorbidities are a growing health epidemic. Interactions between genetic background, the environment, and behavior (i.e., diet) greatly influence organismal energy balance. Previously, we described obesogenic mutations in the gene Split ends (Spen) in Drosophila melanogaster, and roles for Spen in fat storage and metabolic state.
 An RNA Pseudoknot Stimulates HTLV-1 Pro-Pol Programmed -1 Ribosomal Frameshifting
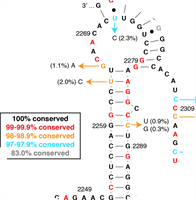
An RNA Pseudoknot Stimulates HTLV-1 Pro-Pol Programmed -1 Ribosomal Frameshifting
January 26, 2020
E. Thulson, E. W. Hartwick, A. Cooper-Sansone, M. A. C. Williams, M. E. Soliman, L. K. Robinson, J. S. Kieft and K. D. Mouzakis
Programmed -1 ribosomal frameshifts (-1 PRFs) are commonly used by viruses to regulate their enzymatic and structural protein levels. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is a carcinogenic retrovirus that uses two independent -1 PRFs to express viral enzymes critical to establishing new HTLV-1 infections.
November 4, 2019
M. A. Cortazar, R. M. Sheridan, B. Erickson, N. Fong, K. Glover-Cutter, K. Brannan and D. L. Bentley
Control of transcription speed, which influences many co-transcriptional processes, is poorly understood. We report that PNUTS-PP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) elongation rate.
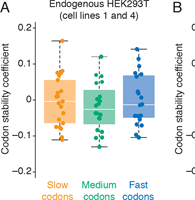
Coding Regions Affect mRNA Stability in Human Cells
September 19, 2019
A. Narula, J. Ellis, J. M. Taliaferro and O. S. Rissland
A new paradigm has emerged that coding regions can regulate mRNA stability in model organisms. Here, due to differences in cognate tRNA abundance, synonymous codons are translated at different speeds, and slow codons then stimulate mRNA decay.
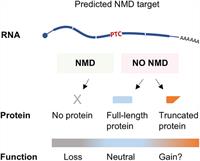
July 31, 2019
M. C. Dyle, D. Kolakada, M. A. Cortazar and S. Jagannathan
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD) is an evolutionarily conserved RNA quality control process that serves both as a mechanism to eliminate aberrant transcripts carrying premature stop codons, and to regulate expression of some normal transcripts.
Classical and Emerging Techniques to Identify and Quantify Localized RNAs
May 3, 2019
J. M. Taliaferro
In essentially every cell, proteins are asymmetrically distributed according to their function. For many genes, this protein sorting problem is solved by transporting RNA molecules encoding the protein, rather than the protein itself, to the desired subcellular location.
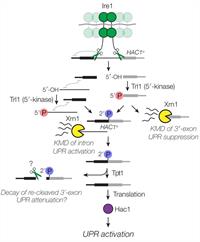
Multiple Decay Events Target HAC1 mRNA During Splicing to Regulate the Unfolded Protein Response
March 16, 2019
P. D. Cherry, S. E. Peach and J. R. Hesselberth
In the unfolded protein response (UPR), stress in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) activates a large transcriptional program to increase ER folding capacity. During the budding yeast UPR, Ire1 excises an intron from the HAC1 mRNA and the exon products of cleavage are ligated, and the translated protein induces hundreds of stress-response genes.