Welcome to Adams Research Lab
Lab Director, Douglas J. Adams, Ph.D.
Our Research
Advancing Bone Health Research at Adams Lab, University of Colorado
| We are identifying genes that regulate bone strength and matrix quality. We use the Heterogeneous Stock Rat population to perform high-resolution gene mapping of hierarchical phenotypic traits defining bone strength, structure, and matrix composition. Our goal is to identify novel genes and pathways involved in regulating bone strength and quality, providing new candidate targets for the treatment of osteoporosis. | 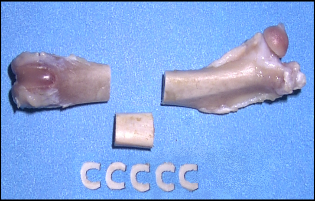 |
| Identifying genes that regulate the response of bone to PTH We use the Diversity Outbred mouse population to perform high-resolution gene mapping of hierarchical phenotypic traits defining bone strength, structure, and matrix composition. Our goal is to identify genes, and interactions among genes, that are involved in the anabolic response to PTH therapy so that treatment decisions for osteoporosis can be made with greater precision for each individual. | 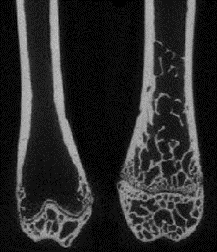 |
| Articular response to altered joint loading Osteoarthritis initiates and progresses amidst daily cumulative joint use. Although joint tissues and cells maintain homeostasis within a range of articular forces and mechanical stress states, extreme impacts and periods of disuse are detrimental to cellular function. We use fluorescent reporters to study the response of cells comprising articular joints to altered stress states associated with disuse, repeated impacts, and joint instability. Our goal is to elucidate the temporal recovery required to prevent a “tipping point” beyond which tissue degradation is not recoverable. | 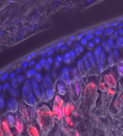 |
| Molecular & Cellular Biology of Fracture Repair The healing cascade in fracture repair involves myriad cellular lineages that differentiate and process a multitude of molecular cues to replace the entire region surrounding a fracture through the formation and remodeling of the fracture callus. Some fractures that do not repair lack an explanation of a poor repair response. We study the temporal process of fracture repair through the lens of cellular differentiation and molecular mechanisms involved in the repair process, using genetic manipulation of specific molecular pathways that are putatively involved at various stages of fracture repair. Our goal is to understand the bone wound healing process to improve healing in cases where fractures do not repair. | 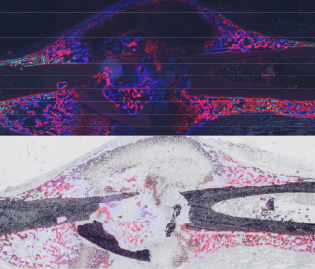 |
| Potential Relief for Dry Mouth Syndromes The incidence of xerostomia (dry mouth) due to reduced saliva production is associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome, radiation treatment of head/neck cancer, and side effects of many medications. Lack of saliva production causes discomfort, pain, tooth decay, and fungal infection. Together with UConn Health colleagues, Dr. Adams is developing a dental implant with patented internal mechanisms for harvesting and delivering physiological fluid from jaw bone marrow spaces and delivering it intra-orally for relief of xerostomia. | 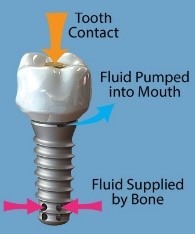 |