Breast Cancer Surgery
Our team of board-certified oncologists will work with you to determine the best course of action to identify, treat and remove cancer from your breast, lymph nodes and other affected areas. Read through the common procedures list below to better understand the breast surgery options provided at the University of Colorado.
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND)
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND) is a surgery that removes an average of 10-20 lymph nodes under your armpit. It is performed to remove known cancer in both the affected and surrounding lymph nodes. After the surgery, all the lymph nodes removed will be tested for cancer cells to determine the best follow-up treatments.
Excisional Breast Biopsy
An excisional breast biopsy is a surgical procedure to remove abnormal breast tissue if you have a lump in your breast that needs to be examined or if a mammogram or ultrasound reveal a lump or lesion you cannot feel. Additionally, the procedure may be recommended if you experience nipple discharge.
An excisional biopsy is often recommended because more information about the lump or lesion in your breast is needed to make an accurate diagnosis. Most breast lumps are benign. If the tissue sample shows cancer, your doctor will explain the biopsy results and discuss the best treatment plan for you.
Lumpectomies
A lumpectomy is surgery to remove a cancer in your breast. Breast tissue that surrounds the cancer will also be taken; this is referred to as the margin. A lumpectomy is also known as breast-conserving surgery, a partial mastectomy, or a segmental mastectomy. The abnormal tissue removed is sent to the lab for pathology examination. Results are usually back within one week.
Mastectomies
A mastectomy Is surgery to remove your breast. A mastectomy is done to treat breast cancer and prevent cancer from spreading. A mastectomy can also be done to prevent breast cancer if you are at high risk.
The type of mastectomy you need may depend on the size of the tumor and whether the cancer has spread.
Simple mastectomy without reconstruction: some patients are not candidates or choose not to have reconstruction and thus have their breast removed without it. This surgery will leave a flat chest. A post-mastectomy bra and prosthesis can be prescribed.
Mastectomy with reconstruction: you will meet with a plastic surgeon to discuss which reconstruction procedure is right for you. There are different types of mastectomies that can be performed with reconstruction. Your breast surgeon will review these options with you.
- Simple mastectomy with reconstruction: the majority of the skin and nipple are removed.
- Skin sparing mastectomy with reconstruction: the skin is preserved but the nipple and areola are removed.
- Nipple preserving mastectomy with reconstruction: all of the skin including the nipple and areola are preserved.
To learn more about reconstruction options, please visit the breast cancer reconstruction tab.
Sentinel Lymph Node Dissection (SLND)
A sentinel lymph node (SLN) is the first set of draining lymph nodes of the breast tumor, usually found in the armpit. A biopsy is a surgery used to find and remove these lymph nodes. Two types of dyes are used to find the sentinel lymph nodes. After the surgery, the lymph nodes will be tested for cancer cells. If the test is positive, it may mean that breast cancer has spread outside of your breast.
Targeted Axillary Dissection (TAD)
Targeted Axillary Dissection involves removing a lymph node that was previously marked with a Savi Scout because it contained cancer. The Savi Scout is a radar-based reflector that is small, similar to the size of a grain of rice. The Savi Scout is placed into your axillary lymph node at least one day before your surgery date. In the operating room on the day of your surgery, your surgeon will use a device that detects the Savi Scout. This will guide your surgeon to the lymph node that needs to be removed. The Savi Scout will be removed during your surgery.
Wide Local Excision
A wide local excision is a surgical procedure to remove an abnormal lump in the skin or immediately deep to the skin in your breast or area around the breast. Wide local excisions are recommended if you have a lump in the skin of your breast that needs to be examined or if a mammogram or ultrasound of your breast finds a lump or lesion you cannot feel.
For women who have had a prior mastectomy, a wide local excision is recommended if there is a lump in the skin that is cancerous or suspicious for breast cancer. Often, a needle biopsy, also called core biopsy, is performed first to determine if surgery is necessary. Alternatively, a skin biopsy, or punch biopsy, is performed in the office to determine if surgery is necessary.
For more information on cancer-related procedures, click the button below to visit the Cancer Center breast website.
Cancer Center Breast Website
Breast Cancer Reconstruction
Our board-certified surgeons are prepared to help you on your breast cancer journey, from diagnosis through post-mastectomy reconstruction. Using the most advanced technology and approaches, our surgeons will work with you to develop an individualized care plan that suits your needs through this difficult time.
Click here for our full Breast Reconstruction Patient Guide.
Click the button below for before/after photos of breast cancer reconstructions completed by University of Colorado surgeons. Images may contain graphic content not suitable for all audiences.
Before/After Photos
Click the button below for before/after photos of breast cancer reconstructions completed by University of Colorado surgeons. Images may contain graphic content not suitable for all audiences.
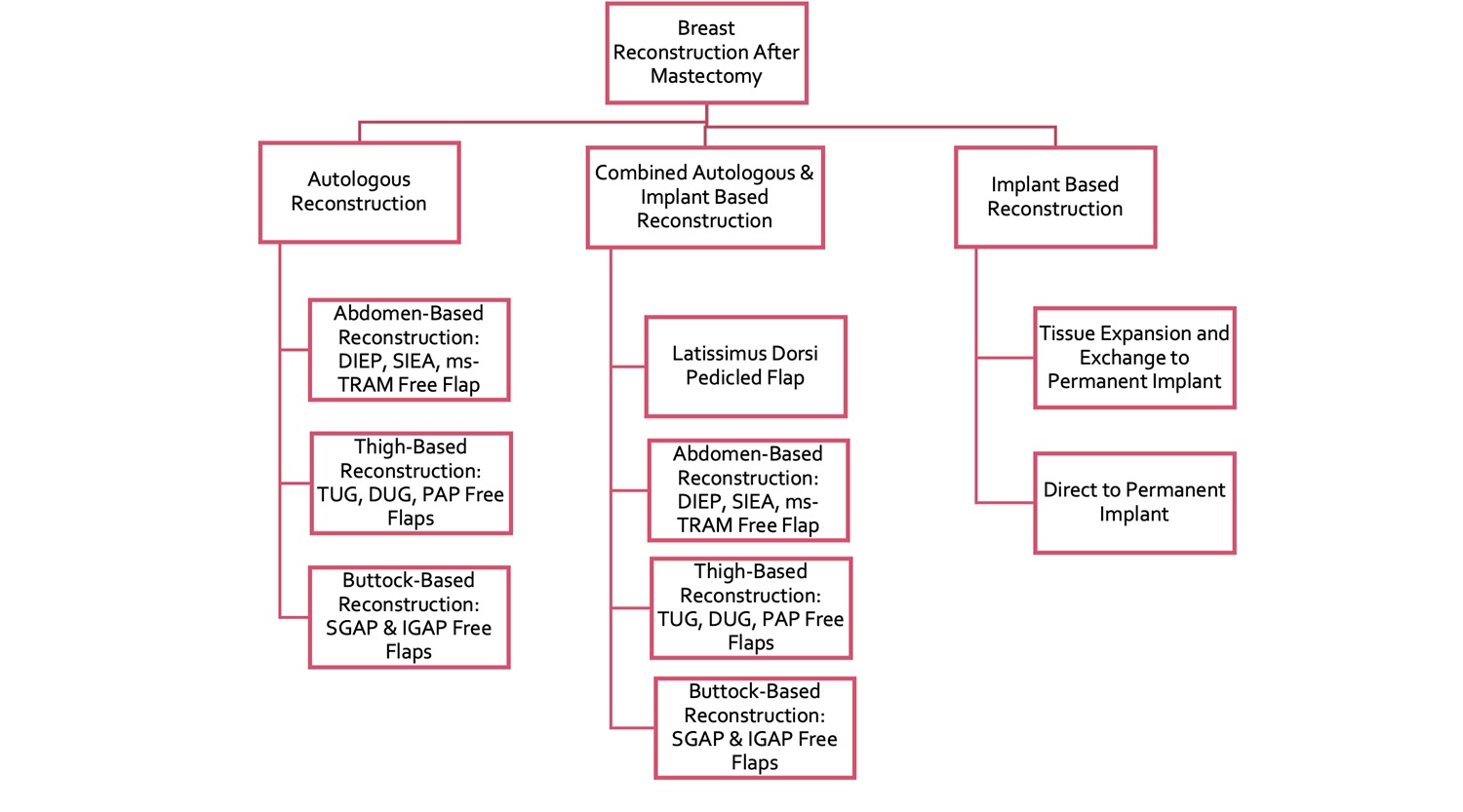
Autologous Tissue Reconstruction
Autologous breasts reconstruction consists of moving tissue (flap) from one part of your body to reconstruct the breasts. Flap tissue can be taken from the abdomen, back, thigh or buttocks. There are two types of flaps that may be used, which are classified according to the attachment of the blood vessels.
1. Pedicled flap: the artery and vein remain attached to the tissue that will be transferred.
2. Free flap: the artery and vein are disconnected with the tissue from the donor site and reconnected in the chest.
The main benefits of autologous reconstruction are that in the majority of cases you do not need an implant, and the reconstructed breasts have a similar shape and feel of your native breasts. Another benefit is that the donor site will have a better contour since redundant tissue is removed. Disadvantages are that they are technically difficult, and there is a very small risk that the reconstruction fails (the tissue that was used to recreate the breasts does not survive).
Click here to learn more about all autologous tissue reconstruction options.
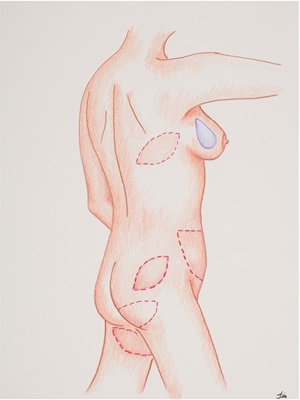
Implant-Based Reconstruction
There are breast reconstruction options that offer a satisfactory cosmetic outcome without having to take tissue from another part of the body. There are many options surrounding the type of implant you may choose including fill, size, shape, and profile. Despite previous controversy regarding silicone implants, they are FDA approved for breast reconstruction.
Click here to learn more about implant-based reconstruction options.
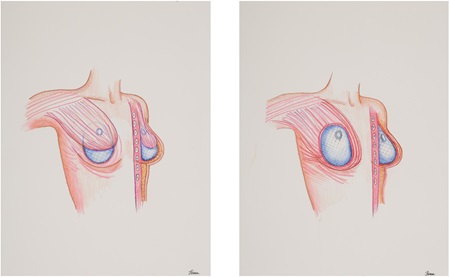
Nipple and Areola Reconstruction
Nipple reconstruction is a surgical procedure to rebuild the nipple and areola, typically on a reconstructed breast. Nipple reconstruction helps give the nipple a more natural color and appearance.
The nipples are created by your plastic surgeon with local tissue rearrangement. They will not react to temperature or touch, will not become flat or larger, and they will not have feeling. Depending on the reconstruction and the appearance of the nipple on the unaffected breast, the reconstructed nipple may look asymmetric. There are a variety of technique that may be used to reconstruct the nipple, which should be discussed with your plastic surgeon.
The areola (colored portion around the nipple) is reconstructed with tattoo or a skin graft from the groin, thigh, or other areas. Areolar tattooing is typically painless because your reconstructed breasts do not have sensation, and may be performed in the office. Tattooing may need to be re-applied after a few years. A skin graft may be taken from your inner thigh or lower waist. The skin from this area has a tendency to heal darker when taken as a skin graft. A skin graft would require you to return to the operating room.
Nipple Tattooing
If you are not a candidate for nipple reconstruction, you can opt to have tattooing done to give the appearance of a nipple. In this procedure, the areola (colored portion around the nipple) is reconstructed with tattoo or a skin graft from the groin, thigh, or other areas. Areolar tattooing is typically painless because your reconstructed breasts do not have sensation, and may be performed in the office. Tattooing may need to be re-applied after a few years. A skin graft may be taken from your inner thigh or lower waist. The skin from this area has a tendency to heal darker when taken as a skin graft. A skin graft would require you to return to the operating room.
Oncoplastic Reconstruction
If you are considering lumpectomy for treatment of your breast cancer, oncoplastic reconstruction may be an option. Done at the same time as your lumpectomy, this surgery can preserve the appearance of the affected breast, and provide balance and symmetry with tissue rearrangement on the unaffected breast. We encourage you to schedule a visit with the plastic surgeon prior to receiving radiation treatment as your options for reconstruction are more limited after radiation therapy.
Symmetry Reconstruction
If you are considering lumpectomy for treatment of your breast cancer, there are procedures that can be done to improve the appearance of both the breast receiving treatment and the unaffected breast. Liposuction or fat grafting, breast reduction, breast lift or breast augmentation may be performed. We encourage you to schedule a visit with the plastic surgeon prior to receiving radiation treatment as your options for reconstruction are more limited after radiation therapy.
Breast Procedures
Our board-certified surgeons utilize leading surgical approaches to help you look and feel your best. Using the most advanced technology, our surgeons will work with you to develop an individualized care plan that suits your breast surgery needs.
Click the buttons for before/after photos of breast surgeries completed by University of Colorado surgeons. Images may contain graphic content not suitable for all audiences.
Breast Reduction
Breast reduction is a surgical procedure that removes excess breast tissue in women or men. In women, this is referred to as reduction mammoplasty and is performed to relieve back, neck or shoulder pain in women with large breasts.
Before/After Photos
Cosmetic Procedures
When a breast surgery is not covered by medical insurance, it is often referred to as cosmetic. We offer self-pay cosmetic breast procedures like breast implants or breast lifts. Click here to be directed to our cosmetic clinic to learn more about our cosmetic services and to see before/after photos.
Cosmetic Clinic Site
Gender-Affirming Top Surgery
For patients who are undergoing gender transformation, we offer male-to-female (MTF), and female-to-male (FTM) top surgeries.
Before/After Photos
Male Breast Reduction
Gynecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction, is intended to reduce the volume and excess skin of the chest. The goal is to improve the contour of the chest wall.
Revision Surgery
If you have undergone breast surgery and are no longer satisfied with the results, our surgeons can help you understand what your options are for modifying your results.
This list describes a few of the breast surgeries we offer. To learn more about what surgery techniques we offer, please schedule a consult with your Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon.
Click here to see before and after photographs of various surgical procedures listed on this page.