Welcome to Zuscik Lab
Lab Director, Michael Zuscik, PhD
Our Research
Zuscik Lab
Impact of Obesity on the Skeleton
Key discoveries made by our group have documented the pathological impact of obesity and on the musculoskeletal system. We have begun to understand the tissue and molecular basis underlying accelerated OA, delayed bone healing, and reduced skeletal bone mass in the obese context. We have documented that insulin resistance and chronic inflammation are key mechanisms of pathogenesis, and we have now discovered that dysbiosis of the gut microbiome in obesity may be a key root cause of these orthopedic problems. Identification of the tissue and molecular mechanisms in each of these situations has energized the assembly of a programmatic team of investigators that work collaboratively to unravel the novel idea that gut microbiome-skeletal interactions are important in homeostasis and disease.
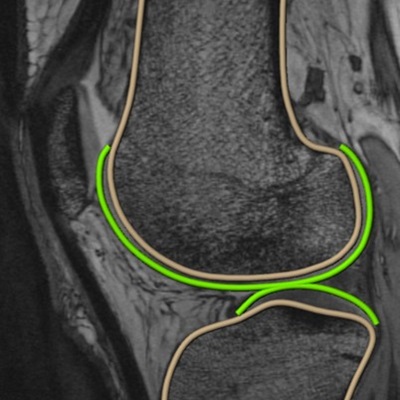
Role of the Gut Microbiome in Osteoarthritis
The gut microbiome is composed of diverse microbial ecosystems that exist in the gastrointestinal tract that have endocrine and immunological functions. We have recently established that dysbiosis, a shift from a “normal” gut microbiome, is associated with musculoskeletal disease, particularly osteoarthritis. Our lab’s work to establish a link between gut flora and osteoarthritis has uncovered the potential to target the gut microbiome to address joint degenerative disease. Currently, we are pursuing a deep study of the gut-joint axis, and in the process, we have developed strategies with preclinical efficacy in sculpting the microbial community in a manner that delays joint degeneration. We are currently testing one such strategy in symptomatic early-stage osteoarthritis in a human clinical trial.
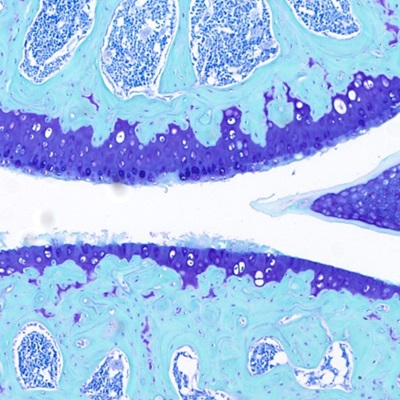
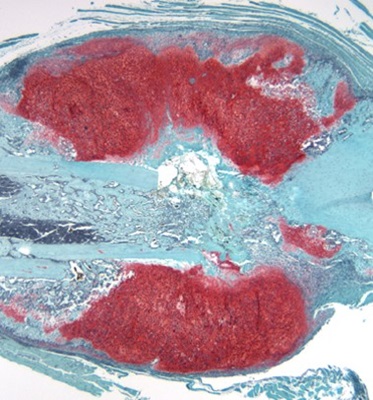
Development of chondroregenerative therapy for osteoarthritis
Activation of the parathyroid hormone receptor (Pth1r) in chondrocytes is known to inhibit cell differentiation and activate the production of the cartilage matrix. Our group discovered that in injured and degenerating cartilage, Pth1r is upregulated in chondrocytes, priming them to respond to agonist peptides. Moreover, we have established that activation of Pth1r by teriparatide (FDA-approved Forteo) is chondroregenerative in a murine model of posttraumatic osteoarthritis. Our current work is focused on mapping the signaling pathways involved with the regenerative effects of teriparatide, and we are testing its potential disease-modifying capability in early-mid-stage human osteoarthritis in an ongoing clinical trial. We are also pursuing experiments with another Pth1r agonist, abaloparatide (FDA-approved Tymlos), in murine models of osteoarthritis.