Neural Engineering & Human-Device Interface
Neural engineering is an interdisciplinary field that combines principles from neuroscience, engineering, computer science, and mathematics to study, repair, replace, or enhance neural systems. It aims to understand the function of the nervous system, develop technologies to interact with it, and create devices that can restore or improve neural function.
Key areas of focus in neural engineering include:
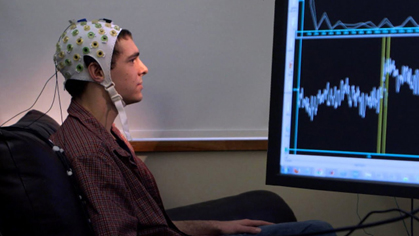
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): These systems enable direct communication between the brain and external devices. BCIs can be used for a variety of applications, such as helping individuals with paralysis control prosthetic limbs or computers using their thoughts.
- Neuroprosthetics: These are artificial devices that replace or enhance the function of damaged or missing neural systems, such as cochlear implants for hearing loss or retinal implants for vision restoration.
- Neural Signal Processing: This involves the analysis and interpretation of signals from the nervous system, which can be used to better understand brain function or to control neuroprosthetic devices.
- Neuromodulation: Techniques like deep brain stimulation (DBS) or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) are used to modulate neural activity, often for the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Neural Tissue Engineering: This area focuses on creating biological substitutes that can restore, maintain, or improve neural tissue function, often through the use of stem cells or biomaterials.
- Cognitive and Behavioral Neuroscience: Neural engineering also overlaps with cognitive neuroscience, exploring how engineering principles can be applied to study or influence cognition and behavior.
The field is highly collaborative, requiring expertise from various domains to innovate in understanding and manipulating the nervous system, ultimately leading to new therapies and technologies that improve human health and capabilities.
Neural Engineering encompasses many technologies and study areas. These are a few of the more well known technologies:
Conditions which can be treated with Neural Engineering Technologies
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD):
- TMS is FDA-approved for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression. It is often used when patients do not respond to antidepressant medications. TMS can target the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), a brain region associated with mood regulation.
- DBS (Deep brain stimulation) is being studied with this condition.
Anxiety Disorders:
- TMS is being explored as a treatment for anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- DBS (Deep brain stimulation) is being studied with this condition.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
- The FDA has also approved DBS and TMS for treating OCD, targeting specific brain circuits involved in the disorder.
Chronic Pain:
- TMS has shown promise in treating chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain, by modulating pain-related brain networks.
Neurological Disorders:
- VNS (Vagus Nerve Stiumlation), TMS and DBS are being investigated for potential use in conditions like Parkinson's disease, stroke rehabilitation, and epilepsy, MS and more.
Migraine:
- TMS can be used as a preventive treatment for migraines or to alleviate symptoms during a migraine attack, with devices designed for home use.
- Advantages of Neural Engineering Technology
Non-Invasive: many (not all) of the technologies are non invasive and do not require surgery or implantation of devices. - Well-Tolerated: Side effects are generally mild and may include scalp discomfort or headaches.
- Targeted Treatment: These state of the art technologies usually allow for precise targeting of specific brain regions, minimizing the risk of affecting non-target areas.
Limitations and Considerations
- Cost and Accessibility: TMS therapy can be expensive and may not be widely available in all areas. Insurance coverage can also vary.
- Treatment Duration: Some technologies last longer than others.
