Shared Content Block:
Surgery Styles -- directory
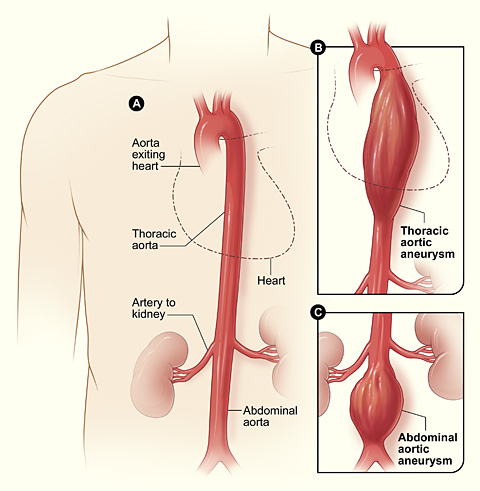
Image courtesy of the National Institutes of Health.
As an aneurysm grows, it can significantly weaken the aorta. In some cases, an aneurysm can burst, causing dangerous bleeding inside the body. Surgical repair may be recommended if the aneurysm is large and likely to rupture.
An aneurysm can occur in any portion of the aorta butis most commonly found in the part of the aorta running through the abdomen. These aneurysms are called Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms or AAA's.
An aneurysm on the portion of the aorta running through the chest, or thorax, is called a Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms account for about 25% of aortic aneurysms and may be the result of injury or trauma to the chest.
There are two types of surgery to repair aortic aneurysms: Open and Endovascular.
- Open surgery for aortic aneurysm repair involves accessing the aneurysm through a major incision (6-10 inches in length) in the abdomen or chest, depending upon the location of the aneurysm. In this type of procedure, the portion of the aorta containing the aneurysm is removed and replaced with an artificial graft.
- Endovascular surgery for aortic aneurysm is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which a catheter containing a stent graft is inserted into an artery in the groin. The catheter and stent graft are then guided into the aorta and to the exact location of the aneurysm. Next, the stent graft is expanded inside the aneurysm, reinforcing the compromised section of the aorta to prevent further damage and/or rupture. This procedure is commonly referred to as a Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair or TEVAR.

Pathology slide of an aortic dissection. This damaged aorta was surgically removed and replaced by an artificial vessel.
Aortic dissection occurs when a small tear develops in the wall of the aorta. The tear forms an additional pathway for blood flow within that section of the aorta and causes the layers of the aorta to separate and weaken.
Aortic dissection is a serious condition. In some cases, the tear can extend through all layers of the aorta, resulting in massive blood loss and death.
Chronic high blood pressure, Marfan Syndrome, or atherosclerosis may increase your risk for aortic dissection.
Surgical treatment for aortic dissection involves the removal of the most severely damaged portion of aorta and replacement of the damaged section with a graft.
An alternative, minimally invasive approach is thoracic endovascular aorta repair. In this procedure, a stent graft is inserted via catheter inside the damaged portion of the aorta to strengthen it and prevent blood from flowing between the layers of the aortic wall.

David A. Fullerton, MD
Professor, Cardiothoracic Surgery
John T. M. Wright Endowed Chair in Heart Valve Surgery
Chief, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery
Appointments and Information
This information is provided by the Department of Surgery at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. It is not intended to replace the medical advice of your doctor or healthcare provider. Please consult your healthcare provider for advice about a specific medical condition.


